Network capacity
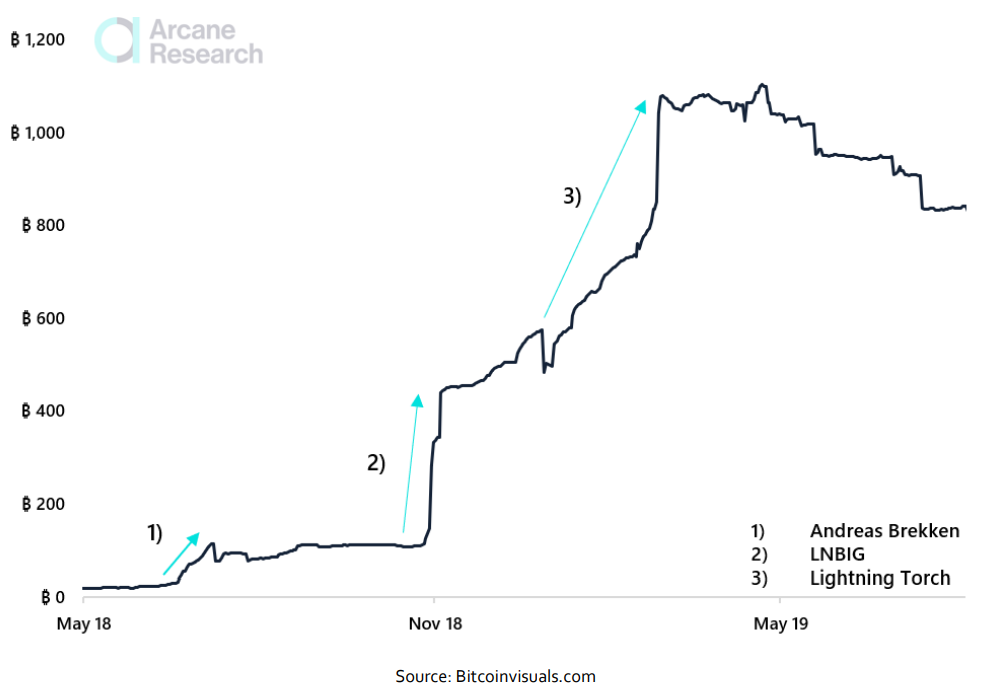
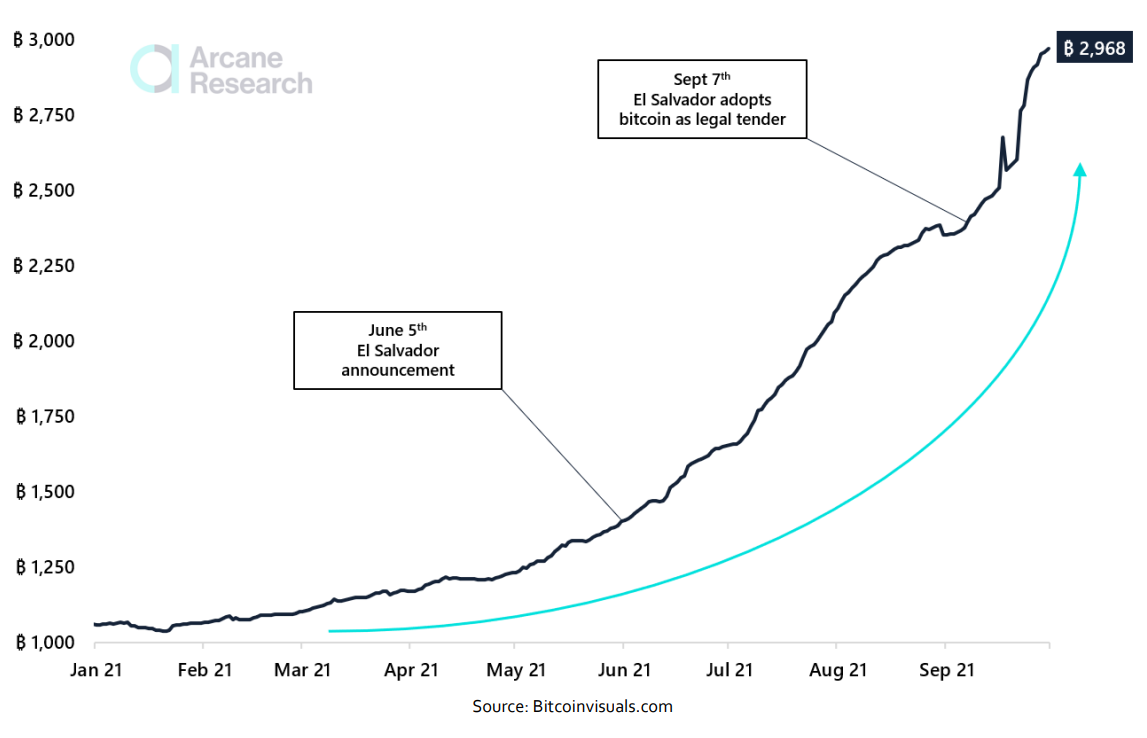
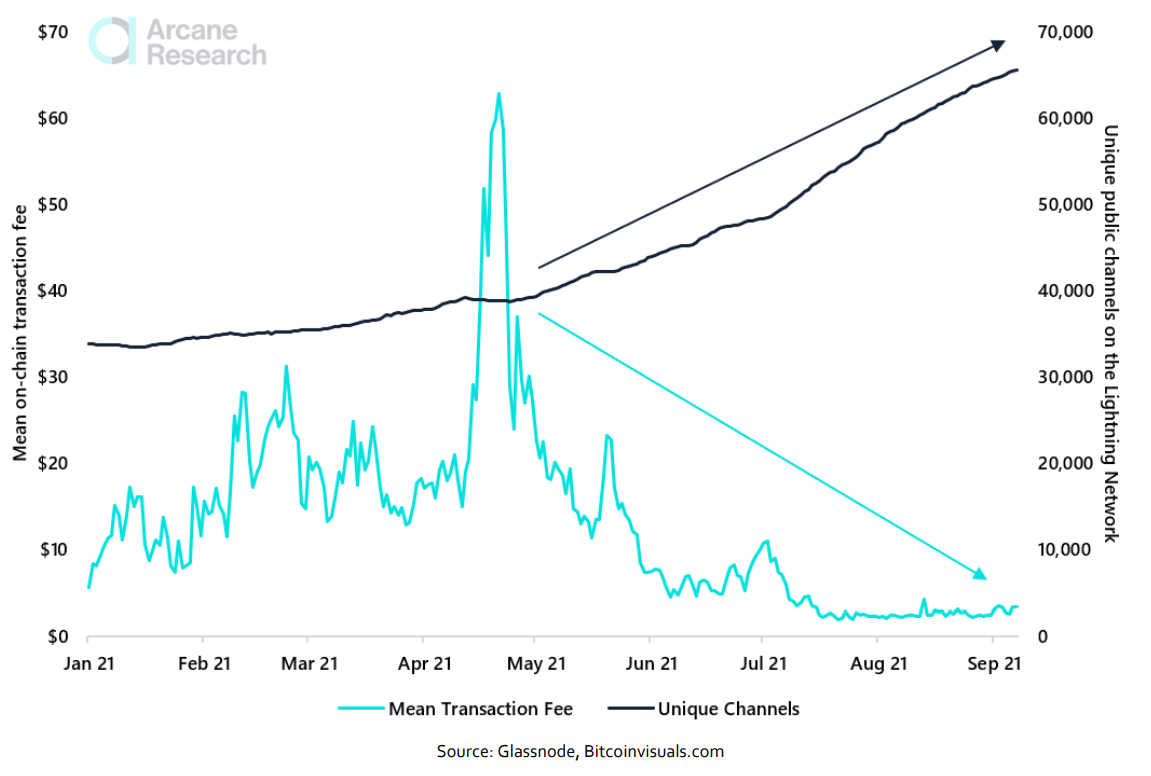
In its nearly three-year history, the Lightning Network has grown to hold a bitcoin capacity of almost 3,000 BTC, with about 17,000 nodes operating on the network and 73,700 unique channels connecting nodes from across the globe. As of late September 2021, the public bitcoin capacity on lightning equals more than $120 million, with users across the world finding value in the option to conduct near-instant small payments at very negligible fees.Lightning Network: BTC Capacity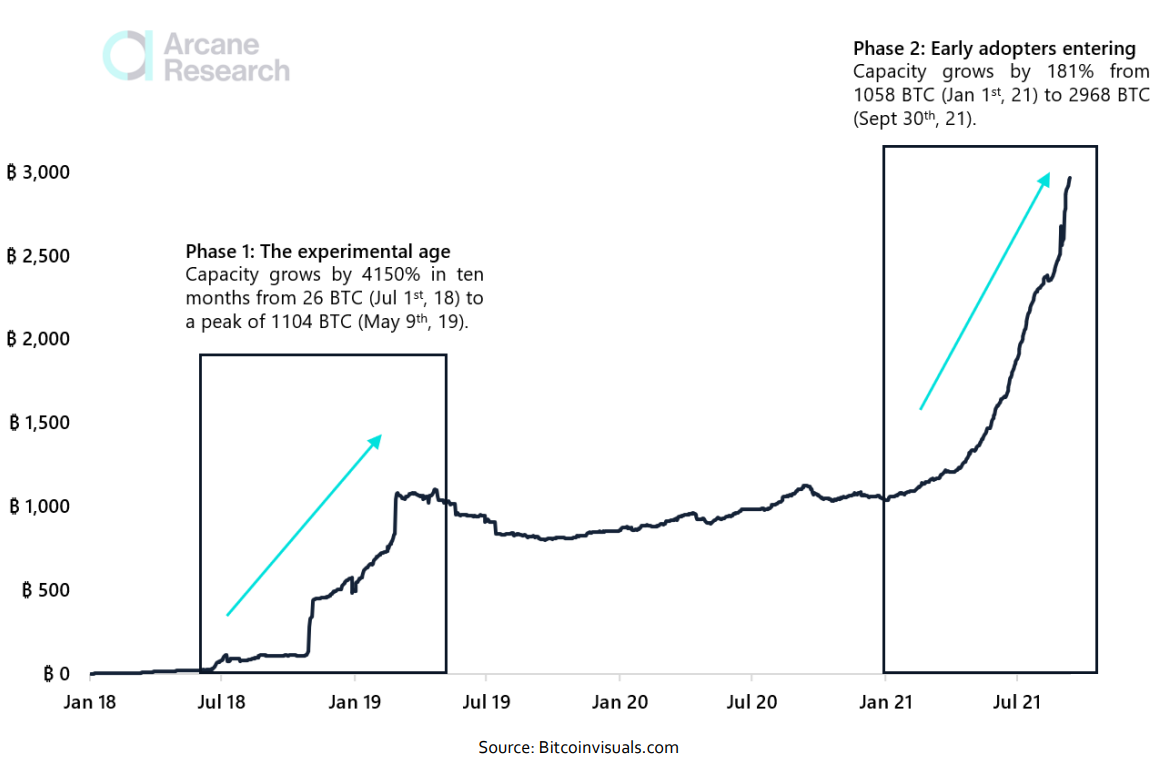
Preview
Preview
Preview
Preview
Lightning scales Bitcoin
The Lightning Network is a powerful second-layer scaling solution for bitcoin, as illustrated below, depicting how Lightning transactions free up block space on the Bitcoin blockchain. The chart is based on estimated transaction data from commonly used wallets on the Lightning Network. We count all transfers to and from wallets in our estimate of the number of Lightning transactions and do not count routing transactions. We are confident that our estimate is close to the actual transaction numbers from these wallets but emphasize that our estimates are, indeed, estimates. Further, the chart assumes that an average Bitcoin block consists of 2000 transactions.Estimate of Blocks / Blocks Days Saved per Month Through Lightning Transactions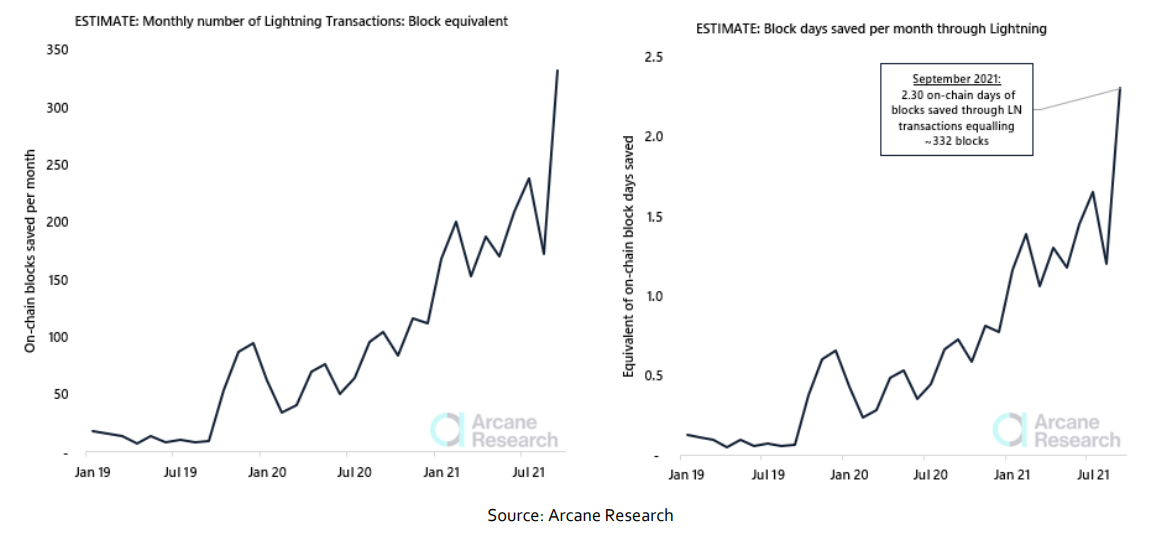
Preview
A centralized network?
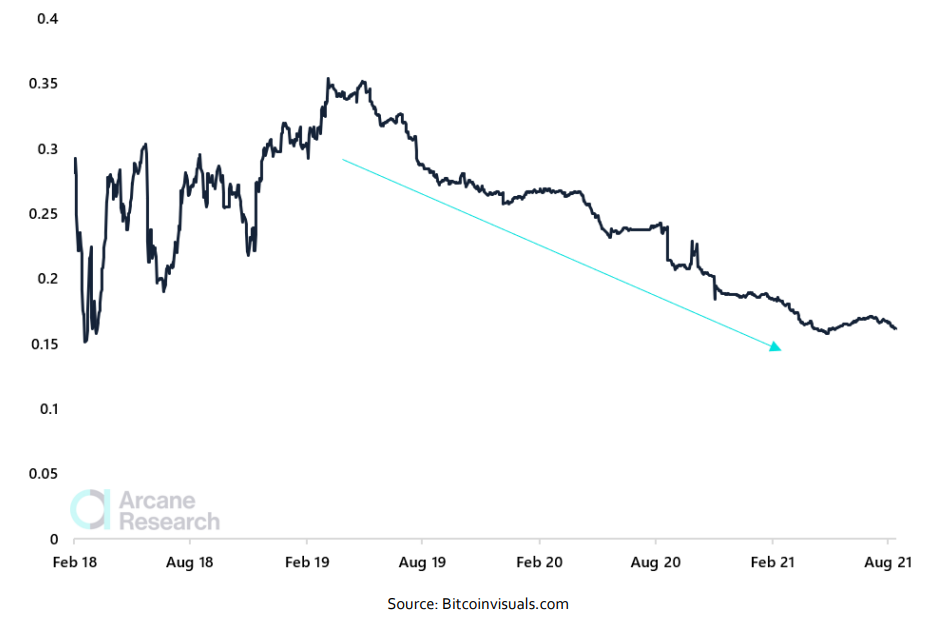
One of the key ingredients in the Lightning Network is the payment channels between nodes, allowing users to transfer funds through a series of nodes by using channels, ending up at the desired end-point destination. Lighting’s elegant routing feature does not come without a cost. The network structurally rewards the most well-connected nodes (hereby hubs), where hubs are an essential part of the network. This architecture makes Lightning transactions structurally more centralized than on-chain bitcoin transactions. Nevertheless, this structure is a feature of Lightning, and without this feature, the network would lose its finesse. While the design, to a certain extent, leads to centralization, users are free to open channels to avoid the central hubs. Hubs are merely a very convenient feature of the Lightning Network, making sure the network is connected. Let’s take a deeper dive into the importance of certain nodes and channels on the Lightning Network. Below, we illustrate the number of cut nodes and channels on the Lightning Network. A cut channel is a channel between two nodes that connects different components of the network. This channel's removal would prevent other nodes from having a path. A cut node is the same idea, except it's a crucial node instead of a channel. In the Lightning Network, cut nodes and channels can be seen as weak points of the network as their removal would entirely disconnect two parts of the network. Therefore, they should ideally be minimized. This is especially true for cut nodes with many channels or cut channels of a large capacity, as the network heavily relies on them to function successfully. Lightning Network Cut Nodes & Cut Channels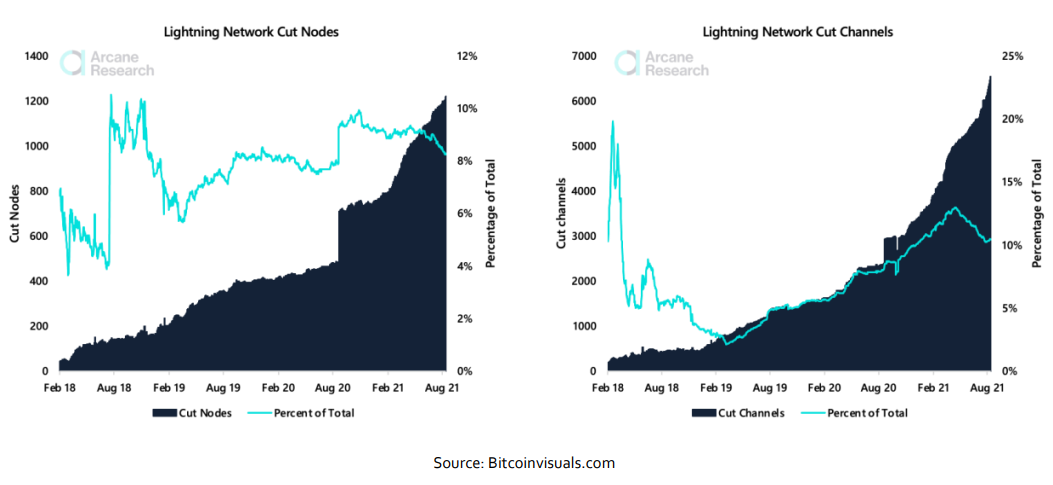
Preview
Preview
