PROPOSED SOLUTIONS TO THE SCALING PROBLEM
Moving transactions off-chain have been a popular proposal to solve the scalability problem. Several projects are striving to unload the pressure from the Bitcoin blockchain. The Lightning Network and Blockstream’s Liquid Network have gained the most traction among the designated off-chain solutions. However, amidst the growth of decentralized finance, a third unexpected platform has taken a significant share of the off-chain market; The Ethereum Network. In this mini report we provide a quick overview of the recent development in the exciting off-chain space.TAXONOMY
In general, a bitcoin transaction can occur both on-chain and off-chain. An on-chain transaction is signed, broadcasted, and settled directly on the Bitcoin blockchain. Off-chain transactions are more intricate and can be categorized into three main categories:1) Layer 2: The transaction is signed but broadcasted to a to a separate network and netted outside of the Bitcoin blockchain2) The “peg out”: The bitcoins are locked on the Bitcoin blockchain and “lifted out” into another system. This system may either be a sidechain (like Liquid and wBTC, which will be introduced later in this report), or a centralized database (like exchanges and custodian wallet providers). 3) Key Transfer: The bitcoin transfer is carried out as a one-time transfer of the private key outside of the Bitcoin blockchainTHE LIQUID NETWORK
The Liquid Network was launched by Blockstream in 2018 as a partial solution to the conundrum of scaling Bitcoin. The Liquid Network is a Bitcoin sidechain that aims to offer fast and confidential transactions between the major trading platforms. Transactions on the Liquid Network are finalized within minutes, with small fees and privacy optionality as the amounts sent can be disguised.Liquid anchors BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain which are then used on the Liquid sidechain as L-BTC tokens, backed 1:1 by BTC. A consortium including Blockstream, several large exchanges and hardware wallets hold the keys to the anchor addresses. Anyone can run a full node on the Liquid Network, but only the members of the consortium are eligible to create new liquid blocks.Liquid targets traders seeking to secure arbitrage profits between exchanges. Short-term price deviations between exchanges often vanish within minutes and by utilizing the fast transfers on the Liquid Network, traders are better positioned to exploit temporary mispricings. Following the launch of L-BTC, the amount of BTC locked into the Liquid addresses grew at a slow pace, but in December 2019 a clear trend shift occurred. Between December 1st 2019 and January 1st 2020 the number of L-BTC jumped by six-fold from 97 L-BTC to 600 L-BTC. The sharp growth has continued and since January 1st the L-BTC supply has increased by more than 400 percent to a total of 2476 L-BTC in circulation, indicating that the Liquid Network is in a state of a S-curve adoption with an influx of traders finding value in Liquids characteristics as a sidechain complement to Bitcoin.THE LIGHTNING NETWORK
The Lightning Network works on top of the blockchain as a second layer payment protocol. Its value proposition is to enable streaming of money; instant off-chain (micro)transactions, in order to avoid blockchain congestion and to make BTC micropayments economically feasible by reducing fees.As a second layer protocol, the Lightning structure differs from other off-chain solutions. Where other solutions operate around a sidechain, a setup where bitcoins are “lifted out” of the Bitcoin blockchain and into another system, Lightning manages valid bitcoin transactions, but outside of the blockchain, in an entirely new infrastructure.The Lightning Network is based around a network of payment channels allowing participants to transfer value to other participants through a routing system, without having to make the transaction public on the blockchain. Initially, participants commit an amount to a payment channel, the funding transaction, which is on the blockchain. This enables the participant to access the Lightning Network.Bitcoin transfers on Lightning can be routed between multiple channels, allowing cheap and near instant transfers. Uncooperative behavior on the Lightning Network is punished through an incentive system, preventing bad behavior from participants.Payment channels on the Lightning Network are based on local consensus, making it possible to open private channels between parties that are not publicly broadcasted. This makes it difficult to measure the exact adoption of and activity on the Lightning Network, but findings by BitMEX Research indicate that 28% of the channels of the Lightning Network are private (as of 28th of January 2020).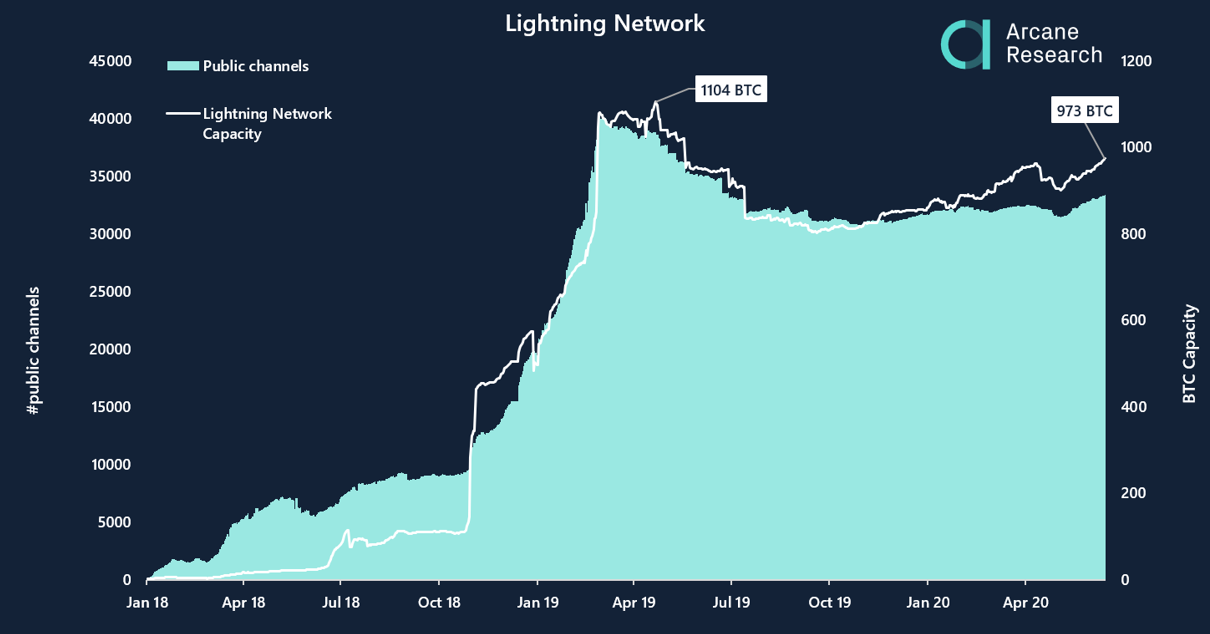
Preview
THE ETHEREUM BLOCKCHAIN – TOKENIZED BTC
Whereas Liquid and Lightning are created as solutions for scaling Bitcoin, an entirely different off-chain destination has spurred amidst the growth of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) - The Ethereum Network.The motivation of tokenizing bitcoin as an ERC-20 token is to enable functionality which is not natively supported on the Bitcoin blockchain, such as compatibility with the Ethereum DeFi ecosystem. A drawdown of tokenized bitcoin on the Ethereum blockchain is the current heavy usage of the Ethereum blockchain, leading to Ethereum fees being larger than Bitcoin fees in periods. If Ethereum successfully switches from PoW to PoS this issue might be reduced, until then tokenized BTC on the Ethereum Network carries similar scaling issues as Bitcoin.The true value in tokenized BTC on Ethereum is the smart contract integration, generating a bitcoin instrument that can be traded on decentralized exchanges and used as collateral on DeFi lending platforms. The hard money properties of bitcoin make it useful in the DeFi system, especially in the lending sector as collateral for loans.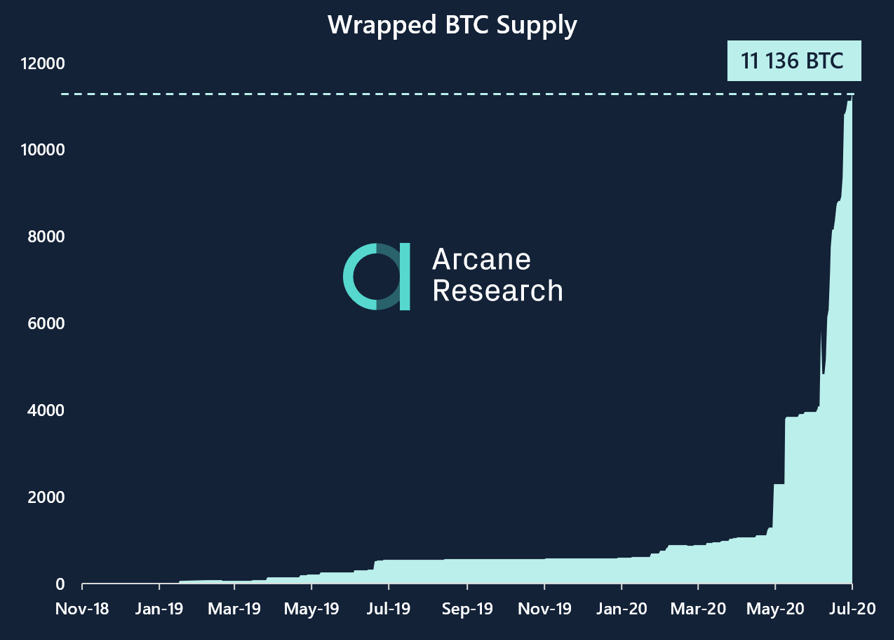
Preview
