Preview
Preview
Quantitative Easing (QE)
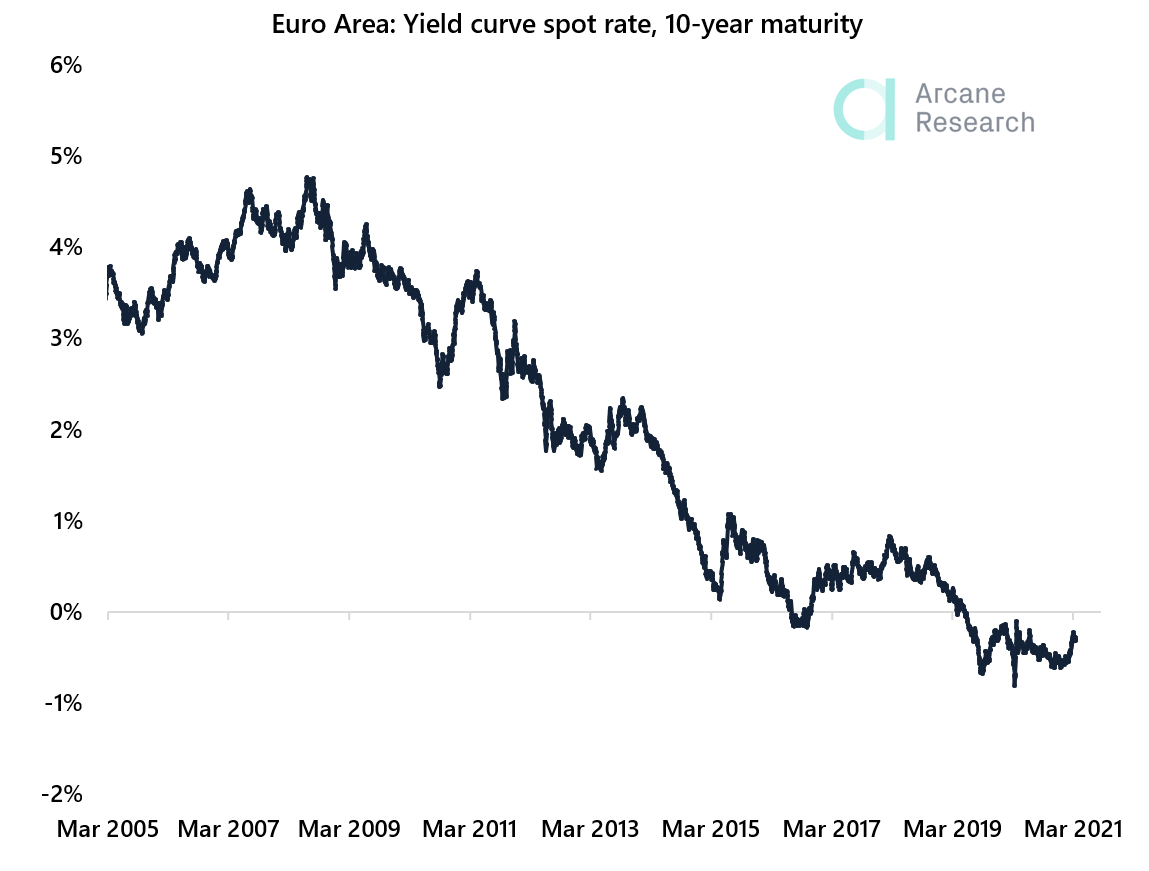
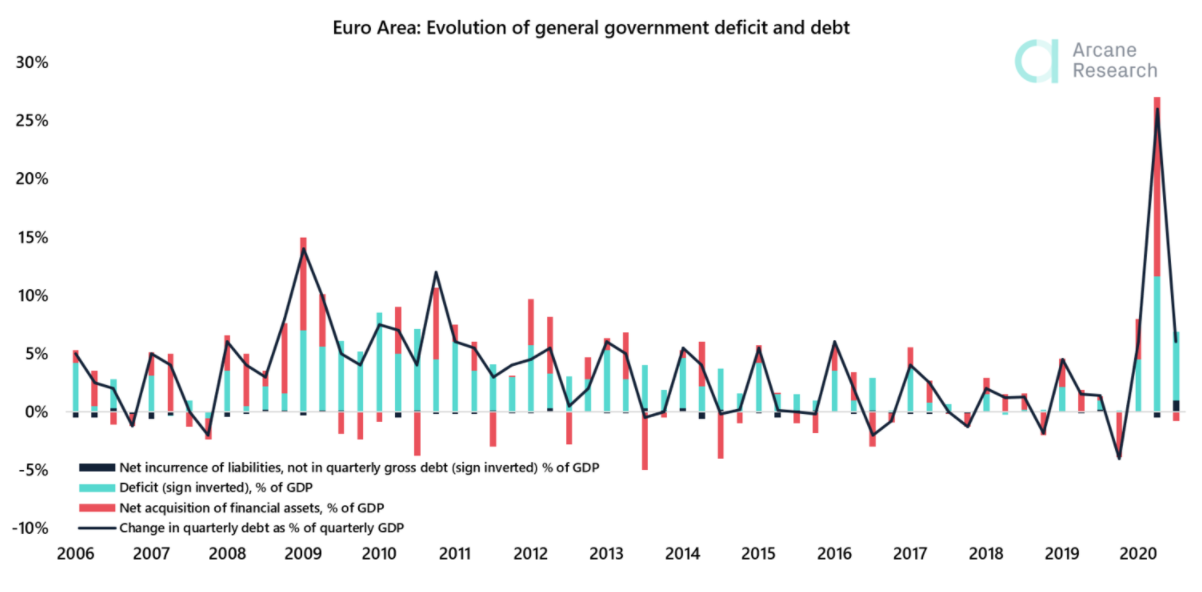
A key principle of monetary policy; to increase the rate of growth in a country, interest rates are cut to encourage consumer spending, thereby increasing the effective demand and ultimately profitability. However, when interest rates are approaching zero, Central Banks are left with the option of injecting money directly into the economy by buying financial securities. This process is known as Quantitative Easing and has the following effects:- Bond prices increase as their demand increases.
- Interest rates are reduced.
- Banks have more money reserved than required, and the money supply in the economy increases.
